- Air & Molded Case Circuit Breakers
- Change Overs
- Contactors & Relays
- Din Rail Components
- Electronic Relays & Controls
- Enclosed Switches
- Enclosure & Distribution Boards
- Energy Efficiency Devices
- Industrial Automation
- LV Panel Accessories
- Motor Control Gear
- Soft Starters
- Power Factor Capacitor
- Variable Frequency Drives
Air & Molded Case Circuit Breakers

Air Circuit Breakers (ACBs) are vital for electrical system safety and reliability, protecting against overcurrents and electrical faults by swiftly interrupting current flow when abnormalities like overloads or short circuits occur. Commonly used in low voltage power distribution systems, ACBs employ adjustable trip settings for tailored application needs, excel at handling high current ratings, and possess a high breaking capacity to interrupt substantial fault currents without damage. Housed in sturdy enclosures, they feature protective elements like thermal and magnetic trip units for enhanced fault protection. Additionally, they often include advanced monitoring, control, and communication capabilities, enabling remote operation.
Molded Case Circuit Breakers (MCCBs) are essential electrical devices, commonly deployed in low to medium voltage power distribution systems, to safeguard circuits against overloads, short circuits, and electrical faults. Encased in non-conductive materials like molded plastic or thermoset materials, MCCBs provide insulation and protection for their internal components. These versatile devices can be customized with adjustable trip settings to meet specific application requirements. MCCBs employ a tripping mechanism, typically based on thermal and magnetic elements, to respond to abnormal conditions, including excessive current levels and short circuits. They offer high breaking capacity, ensuring they can interrupt high fault currents without harm, and their compact design suits limited installation spaces.
We Represent






Change Overs


Changeover switches, also known as transfer switches or selector switches, are electrical switches that allow the manual or automatic switching between two or more power sources or circuits. They are commonly used in electrical distribution systems, backup power systems, and industrial applications where a reliable and uninterrupted power supply is critical. The primary function of a changeover switch is to transfer the load or power source from one circuit to another, ensuring continuity of power supply during power outages, maintenance activities, or when switching between different power sources. Changeover switches often have three positions: “Mains,” “Off,” and “Generator” (or any other alternate power source). The switch enables users to manually select the power source they want to use, or in some cases, it can automatically detect a power interruption and switch to an available backup power source. Changeover switches come in various sizes and configurations to accommodate different voltage and current requirements. They are typically equipped with robust safety features, such as insulation barriers, arc suppression technologies, and interlocking mechanisms, to prevent accidental misconnections and ensure safe operation.
Overall, changeover switches provide essential functionality for maintaining electrical system reliability and enabling seamless power transfer when needed.
We Represent






Contactors & Relays


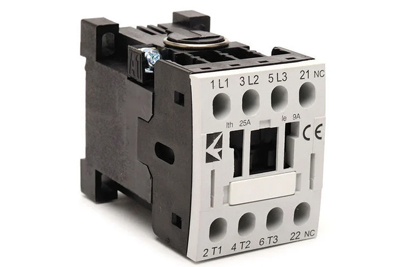
Contactors and Overload Relays are vital components in electrical systems, ensuring equipment protection and safe operation. Contactors act as electromagnetic switches, directing electrical power flow to loads like motors or lighting systems. Comprising a coil and contacts, they engage when a control signal energizes the coil, allowing current to flow. When the signal ceases, contacts open, cutting off the power supply. Contactors are built for high currents and voltages, ideal for heavy-duty tasks. Many feature auxiliary contacts for signaling, control, or interlocking, and some offer added safety elements like overload protection or surge suppression.
Overload relays, conversely, safeguard equipment by detecting and preventing excessive current flow, common in motors or transformers. They defend against overcurrent conditions that can harm or disrupt equipment. An overload relay consists of a current sensor, contacts, and a trip mechanism. If the actual current surpasses a predefined threshold, the trip mechanism activates, opening contacts and disconnecting power to the equipment. This prevents overheating and potential damage due to excessive current, guarding against motor overload, phase loss, and mechanical failures. Overload relays often have customizable settings, adapting to equipment-specific needs.
Contactors and overload relays collaborate in electrical systems, efficiently managing power distribution and safeguarding equipment from overcurrent issues. Their presence is essential for the secure and effective operation of diverse electrical applications.
We Represent






Din Rail Components

DIN Rail components are a type of mounting system used in low voltage (LV) switchgear to securely install and organize various electrical devices and components. This system is based on the DIN standard, which provides a standardized method for mounting and interconnecting components in switchgear assemblies. DIN Rail components are designed to be mounted on a DIN Rail, which is a metal or plastic rail that is commonly installed in switchgear enclosures or control panels. The DIN Rail has a standardized width of either 35mm or 15mm, allowing for easy installation and alignment of the components.
DIN Rail components offer several benefits in LV switchgear installations. They provide a compact and modular solution, allowing for easy installation, rearrangement, and expansion of electrical components. The standardized DIN Rail system ensures compatibility and interchangeability among different components from various manufacturers.
MCBs, RCCBs, RCBOs, Isolators, Contactors, Relays, Protection Devices, Auxiliary contacts, Signalling Devices are the major din rail components that are installed in distribution boards to ensure the proper functioning and protection of electrical circuits within the distribution system.
Overall, DIN Rail components are essential in organizing and mounting electrical devices within LV switchgear, providing a reliable and efficient solution for electrical distribution and control systems.
We Represent






Electronic Relays & Controls

Electronic relays and control products are indispensable components within electrical systems, offering control and protection capabilities crucial for efficient and secure operation. These devices serve as electronic switches, utilizing low voltage signals to control high-power electrical equipment. Their applications are diverse, encompassing circuit switching, motor speed control, equipment safeguarding against overloads or short circuits, and monitoring voltage or current levels. Electronic relays outperform traditional electromagnetic relays, boasting quicker response times, greater accuracy, and enhanced reliability. In summary, electronic relays and control products are pivotal in ensuring the efficient and safe operation of electrical systems. They deliver precise control, protection, and monitoring capabilities, facilitating equipment operation, energy optimization, and heightened safety measures. These products find extensive utility across diverse industries, including manufacturing, power generation, transportation, and building automation.
We Represent






Enclosed Switches


Enclosed switches generally refer to electrical switches that are enclosed within a protective housing or enclosure. These enclosures serve several purposes, including safety, protection against environmental factors, and preventing accidental contact with live electrical components. The primary purpose of enclosing switches is to enhance electrical safety. By placing the switch within a protective enclosure, it reduces the risk of accidental contact with live electrical components. This is particularly important in industrial and commercial settings where high voltage or current may be present.
Enclosed switches are designed to protect the internal components from environmental factors such as dust, moisture, and contaminants. They are often rated for specific environmental conditions, making them suitable for indoor or outdoor use.
We Represent






Enclosure&Distribution borads


Enclosures and distribution boards are vital components in electrical systems, serving to protect and efficiently distribute electrical power while ensuring safety. Enclosures, typically constructed from metal or plastic, provide a protective casing for electrical components and wiring, safeguarding against physical damage, environmental factors, and unauthorized access. They also contain potential short circuits or electrical faults, preventing electrical shocks and fires.
Distribution boards, also known as breaker panels or fuse boxes, are pivotal for power distribution within buildings. They house multiple circuit breakers or fuses, controlling power distribution to various areas or circuits. These boards facilitate organized access to individual circuits, simplifying electrical control and maintenance. Distribution boards are centrally located, offering a systematic method for dividing and safely supplying electricity to different building areas and equipment. Circuit breakers or fuses in these boards act as protective devices against overloads, short circuits, and electrical faults.
Enclosures and distribution boards adhere to industry standards, featuring safety elements like lockable doors, insulation, ventilation, and grounding provisions. They come in diverse types and configurations, such as weatherproof enclosures for harsh environments and explosion-proof enclosures for hazardous areas. Distribution boards vary in size and the number of circuit breakers or fuse positions, accommodating specific power demands.
We Represent






Energy Efficiency Devices


Energy efficiency devices within LV (low voltage) and MV (medium voltage) switchgear are purpose-built to enhance efficiency and curtail energy losses in electrical distribution systems.
One such device is the automatic power factor correction system, commonly found in LV and MV switchgear. It continuously monitors the power factor, and the ratio of real power to apparent power, and automatically tweaks the reactive power to maintain the desired power factor. This process minimizes energy losses from reactive power, ultimately boosting system efficiency and reducing energy expenses.
Intelligent electronic devices (IEDs) or digital relays are another integral component. They oversee various aspects of the electrical system, including voltage levels, power quality, and fault detection. Leveraging advanced digital technology, IEDs optimize switchgear operation by adjusting settings, swiftly detecting and isolating faults, and overall enhancing system efficiency.
These systems continuously gather data on energy consumption, voltage levels, and other parameters in real time. This data empowers operators to identify energy-intensive processes and fine-tune system settings for optimal efficiency. Energy management systems can also implement demand response strategies to trim peak energy demand, further optimizing energy consumption and cost reduction.
We Represent






Industrial Automation


Industrial automation is the application of advanced technologies and control systems to streamline and optimize manufacturing and industrial processes. It involves the use of various technologies like robotics, computer control systems, and artificial intelligence to automate tasks traditionally performed by humans. The primary goal of industrial automation is to enhance productivity, improve product quality, increase efficiency, and ensure safety in industrial settings.
Key components of industrial automation include programmable logic controllers (PLCs), which serve as the central control units, and sensors and actuators that gather data and carry out actions. Human-machine interfaces (HMIs) allow operators to monitor and control the automation processes. Robots and robotic systems are integral for tasks like material handling, assembly, and welding.
Industrial automation finds applications across diverse industries, including manufacturing, automotive, aerospace, pharmaceuticals, and food production. Benefits include reduced labor costs, increased production speed and accuracy, improved consistency, and the ability to operate in hazardous or challenging environments.
We Represent





LV Panel Accessories


Low Voltage (LV) panel accessories are crucial components in electrical distribution systems, providing the necessary functionalities to ensure the safety, efficiency, and reliability of power distribution. These accessories are designed to enhance the performance and versatility of LV panels, which are central hubs for controlling and distributing electricity within buildings, industrial facilities, and infrastructure.
LV panel and distribution board accessories encompass a wide range of electrical components, including tinned copper Bus bars, busbar supports, Panel Wires, Comb busbars and mechanical and electrical accessories. Metering devices provide valuable insights into energy consumption and power quality, aiding in energy management and system optimization. Busbars ensure efficient power distribution within the panel, minimizing energy losses and facilitating easy maintenance and expansion.
We Represent




Motor Control Gear


Motor Control Gear Products are vital components in electrical systems, enabling precise control and protection of electric motors across diverse applications. This category encompasses contactors, overload relays, motor starters, control switches, and related accessories.
Contactors act as the main power switch for motors, handling high voltages and currents in heavy-duty applications. They ensure smooth operation and minimize electrical arcing. Overload relays provide protection against motor overloads, phase failures, and electrical faults by monitoring current flow and tripping the power supply when abnormal levels are detected. This prevents motor overheating and prolongs its lifespan.
Motor starters combine contactors and overload relays into a unified, compact unit, offering easy installation and operation. They may include functions like manual or automatic motor control, thermal protection, and integrated control switches.
Control switches and accessories, such as push buttons and selector switches, give operators a user-friendly interface for motor control. These components meet industry standards, ensuring safety and reliability. They come in various sizes, ratings, and configurations to suit diverse motor sizes and applications. Advanced features like remote control capabilities and surge protection may also be included.
We Represent






Soft Starters


Soft starters facilitate controlled motor starting and stopping by gradually adjusting voltage, reducing initial current surge and mechanical stress. This ensures smooth acceleration and deceleration.
Unlike direct-on-line starting, soft starters apply a gentle voltage ramp, preventing abrupt shocks that could harm the motor or connected machinery. They confer several benefits: prolonging motor lifespan, reducing breakdowns, and enhancing energy efficiency by curbing excessive startup consumption.
Soft starters optimize machinery performance. By regulating torque and speed, they decrease wear and tear, limit vibrations and noise, and improve overall system operation. They also prevent water hammer effects in pump systems, averting potential pipe and valve damage.
These devices come in various types and configurations, tailored to specific motor and load characteristics. They can be integrated into control panels or function as standalone units. Some advanced models feature motor overload and phase protection, along with remote monitoring and control capabilities. Soft starters are a valuable addition to electrical systems, ensuring smooth, controlled motor operation while safeguarding equipment and conserving energy.
Soft starters are essential devices in electrical systems for smooth and controlled motor starting and stopping. They protect motors from excessive stress, improve energy efficiency, enhance system performance, and extend the lifespan of motors and connected equipment. By providing a gradual voltage ramp-up or ramp-down, soft starters ensure a safe and reliable operation of electrical systems in various industrial, commercial, and residential applications.
We Represent




Power Factor Capacitor


Power factor capacitor and reactor are electrical devices used to manage and improve the power factor of electrical systems.
A power factor capacitor is designed to correct a low power factor, which is caused by inductive loads in the electrical system. Inductive loads, such as motors and transformers, draw reactive power from the power supply, resulting in a lagging power factor. The power factor capacitor is connected in parallel to the load and helps to offset the reactive power, bringing the power factor closer to unity (a power factor of 1). This not only helps improve the overall efficiency of the electrical system but also reduces energy consumption and prevents penalties from utility companies.
On the other hand, a power factor reactor is used to correct a high-power factor, which occurs in systems with capacitive loads. Capacitive loads, such as capacitors used in power factor correction devices, can cause excessive leading power factor. In such cases, a power factor reactor is connected in series with the load to offset the excessive capacitive reactive power, thus bringing the power factor closer to unity.
We Represent






Variable Frequency Drives


Variable Frequency Drive (VFDs) is an electronic device used for controlling the speed and torque of an electrical motor by varying the frequency and voltage supplied to the motor. It provides energy-efficient motor control and enables precise regulation of motor speed in various applications, such as HVAC systems, pumps, fans, compressors, and manufacturing equipment. VFDs offer benefits such as energy savings, improved motor performance, reduced wear and tear, and enhanced process control. They are crucial components in industries where precise control of motor speed and energy consumption is required.
We Represent





